Search Results for: analogous structures
Analogous structures
Analogous Structures Definition In evolutionary biology, analogous structures are biological structures having similar or... Read More
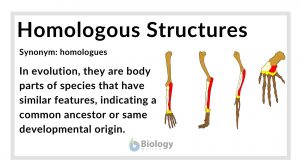
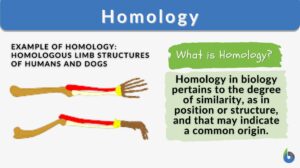
Homologous structures
Homologous Structures Definition What are homologous structures? In biology, homologous structures are physical features... Read More
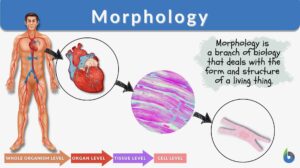
Morphology
Morphology Definition Morphology means the study of the shape and structure of living things from a biological perspective.... Read More
Convergent evolution
Convergent evolution definition What is convergent evolution? Convergent evolution is a concept in evolutionary biology... Read More
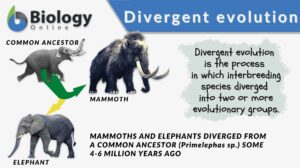
Divergent evolution
Divergent Evolution Definition Divergent evolution refers to the process by which interbreeding species diverged into two... Read More
Homogenous
What is homogenous? What does homogenous mean? The word homogenous has been derived from two Greek words that are... Read More
Nucleoplasm
Definition noun plural: nucleoplasm nu·cle·o·plasm, ˈnjuːklɪəˌplæzəm (cell biology) The protoplasm of the... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and Behavior Having discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
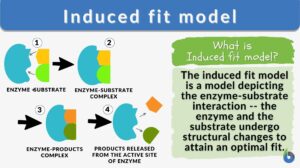
Induced fit model
Induced-Fit Model Definition The induced-fit model is a model for enzyme-substrate interaction to depict the dynamic... Read More
Convergence
Definition noun (evolutionary biology) The evolutionary process in which the organisms evolve bodily parts that are... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Fruits, Flowers, and Seeds
Flowering plants grow in a wide variety of habitats and environments. They can go from germination of a seed to a mature... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
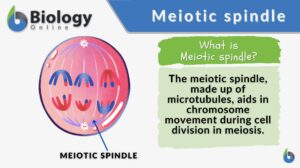
Meiotic spindle
Meiotic Spindle Definition The meiotic spindle refers to the spindle apparatus that forms during meiosis in contrast to... Read More
Blindness – Evolutionary regression? Maybe not!
The recent Netflix's hit flick, Bird Box, surely startled the viewers with the thrilling scenarios revolving around the... Read More
Respiration
Definition noun, plural: respirations Any of the various analogous processes by which there is an exchange of... Read More
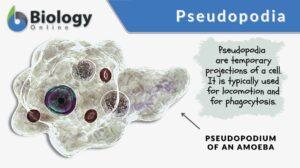
Pseudopodia
A pseudopodium (plural: pseudopodia) refers to the temporary projection of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. Pseudopodia... Read More